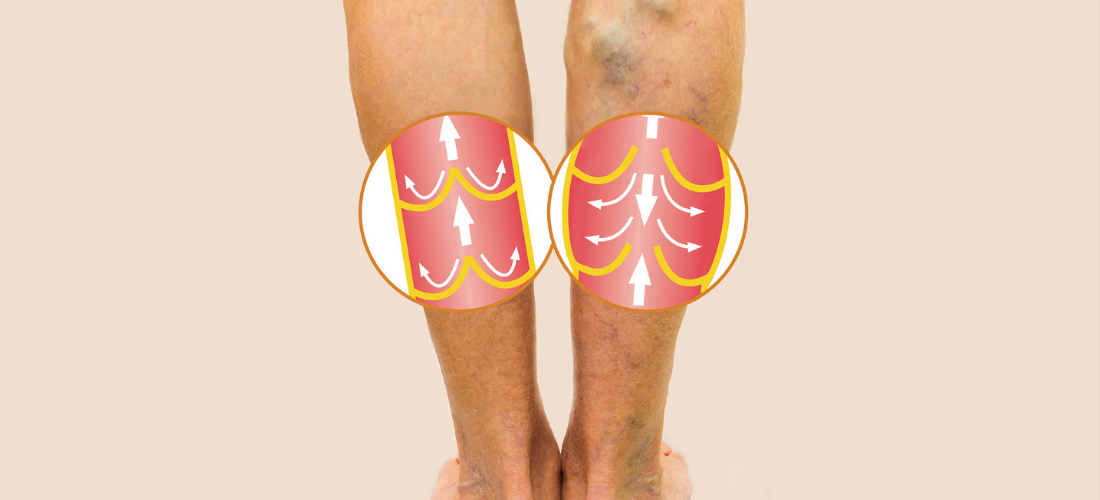
The goal of treating venous diseases is to relieve symptoms and improve the appearance of the affected area.
The first step in the treatment of advanced venous disease involves closing the Greater Saphenous Vein (GSV), a large vein that runs along the inside of the upper thigh. In the past, the vein was removed in a surgical procedure known as vein stripping. Vein stripping procedures are performed in an operating room under general anesthesia and involve a considerable recovery period. However, several less invasive procedures have become more accepted alternatives to treat varicose veins.
Many modern treatment options do not require general anesthesia and are performed in an outpatient setting.
The type of treatment your doctor will recommend depends on several factors including symptoms, severity, and age. Options for the treatment of varicose veins include:
EndoVenous Laser Treatment (EVLT®)
One of the latest varicose veins treatment options, this outpatient, minimally invasive procedure works by eliminating bulging veins at their source. A very small laser fiber is threaded into the vein. Energy from the laser closes the vein, causing the blood to divert to other, healthy veins. The procedure lasts about an hour and is performed without sedation, using local anesthesia.
Surface Laser Treatment
CoolGlide® surface laser treatment uses pulses of light energy to treat spider veins, with excellent results. This therapy can also eliminate small superficial facial veins without bruising. CoolGlide® works by specifically targeting the microvasculature of the skin, the smallest blood vessels and capillaries that tend to damage easily when they are too close to the skin's surface. No anesthesia is necessary and there is no downtime needed after treatment.
Sclerotherapy
Deliver a more dramatic cosmetic result. During sclerotherapy, a liquid "sclerosing" agent is injected directly into the visible vein, which causes the vein wall to swell, stick together, and seal shut. The vein eventually becomes fibrotic scar tissue, and in a few weeks it fades. Additional injections may be required to achieve the desired cosmetic result. Sclerotherapy causes minimal discomfort and anesthesia is not required. Unlike other centers, our Vein Center uses only FDA-approved sclerosing agents. In some cases, a foamed solution of these drugs may be used.
Ambulatory phlebectomy
To perform ambulatory phlebectomy, a local anesthetic fluid is injected into the area of varicose vein clusters. The doctor punctures the skin next to the varicose vein, inserts a small hook into the hole, grasps the vein and removes it. The area is covered with a compression bandage and/or compression stockings. No stitches are required, the scars are nearly imperceptible, and the patient is able to walk immediately following the procedure.
If your symptoms are less severe, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following lifestyle changes:
- Wearing compression or support stockings to help improve circulation and relieve pain or discomfort in the legs
- Losing weight
- Walking regularly
- Reducing salt (if swelling is a problem)